When we think of and talk about the back, we're talking about a huge percentage of the body. It forms the entire posterior region of the torso, and is responsible for the monolithic task of helping us align upright. For that reason, I'm going to talk about it in two posts, one on the spine, and the other on the muscles around it.
Here We Go
The spine, one of nature's many miracles, is made of 33 vertebrae: 24 are stacked and separated by discs, and the last nine (at the base of the spine essentially "inside" the pelvis) are fused together to form the sacrum and coccyx. The 24 movable vertebrae are divided into regions, each of which slightly different characteristics and obligations.
It is particularly important to notice the shape and location of the natural curve of the spine.
The thoracic region is responsible for a great deal of the flexibility, mobility, and rotation we can accomplish; this region's accentuated curve is well-suited to its function for movement.
The lumbar region, made of thicker and larger vertebrae, is designed for weight-bearing support and balance. The lumbar vertebrae are the least flexible, but that does not mean they aren't able to move, they can - it's just not so noticeable to us, much like we don't notice the collar bone's movement when we move our arms. (Read more about that in my article in the October 2015 issue of Rhythm!Scene.)
The cervical region makes up what we think of as the neck, and its vertebrae are tiny in comparison to the lumbar vertebrae. TINY. The top of the spine is meant to balance the head, not to hold it up - that's too much work for those little bones and muscles (more on them later). If you look at the posterior view, you will see two small "ruts" at the top of the cervical vertebrae - this is where the skull balances. The cervical vertebrae, though not meant to hold up weight, are still mobile - try to tilt your head forward, back, and to each side - the cervical vertebrae make this possible.
Here is a diagram showing the relationship of the spine with the pelvis.
I love this diagram for a few reasons:
1- it shows that the sacrum and coccyx extend into the pelvis, descending all the way to the level of the hip joint;
2- it shows the size of the lumbar vertebrae (they are each about a third of the size of an ilium!!!); and 3- the discs between our mobile vertebrae are portrayed as bouncy, vibrant organisms.
More About Discs
The spine is not glued together. A healthy, uninjured spine has dynamic disks between vertebrae, aptly named intervertebral discs. Think of them like shock absorbers. Just like shocks on a car keep it from bottoming out on the potholed lanes of Mass Pike, Storrow Drive, or any other street [not necessarily in Boston], our discs make sure that our strategically-shaped vertebrae don't slam against one another or down onto the pelvis, which could result not only in a slipped disc or broken pelvis, but perhaps a disconnection of the nerves in the spinal column. Particularly when located in the lumbar region of the spine, a slipped disc means incredible discomfort.
Where Does the Weight Actually Go?
To understand where the weight is distributed along the spine, it is best to look at a vertebra individually from a bird's eye view.
The vertebral body is the weight-bearing part of the vertebrae. The spinous process, on the opposite end, is what we can feel with our fingers if we run them up and down the middle of our back. The spinous process actually has nothing to do with bearing weight, but does provide an easy location for muscles and ligaments to attach.
By touching the middle of your own lower back, you can imagine the size of the spinous process, and from there you can imagine the size of the vertebral body and its distance from the spinous process. I imagine there being anywhere from 1.5-2 inches between the tip of the spinous process and where weight is actually distributed throughout my spine.
A correct mental image (see: body map) is key to learning how the spine aligns and balances rather than holds. A common misconception is that "good posture" results from a straight back; from looking at the natural curve of the spine, it is clear that balance is not achieved by a straight line, but instead by properly distributed weight. If we measure the idea of a straight back by imagining the bony protrusions (aka spinous processes) on our backs, we are trying to hold up our entire torso with the attachments of muscles and ligaments rather than balancing it a few inches inward on the long column of stacked vertebral bodies.
The diagram below shows just one example of bad posture. The good posture example shows a more natural spinal curve; you can examine the exaggerated curves of the bad posture model and see that the weight (represented by the vertical line) is placed on the spinous process of the lumbar vertebrae - undoubtedly, this person experiences lower back pain. Notice, too, that the weight is placed on the front of the hip and the back of the neck. This person probably experiences pain there, too.
The example of good posture shows the line of weight distribution closer to the midline of the body, in line with the hip joints, the back of the knee, and the pons at the top of the cervical vertebrae where the skull delicately balances.
Ain't Nobody Have a Waist
The waist is the smallest circumference of the torso. Throughout history we have celebrated the tiny and if they weren't already, we tried to make them appear to be.
What's interesting is that there is no anatomical body part that constitutes as a waist-maker. The waist is an effect of the toning of obliques, lats, abs, and other little muscles that happen to cross at the lower end of the rib cage. This is all probably obvious, but what's interesting is that we sometimes think of this muscular accident as a joint, moving our torsos in relation to it, which makes us look like the bad posture example from above, causing back pain. If we are able to view the bicep as a muscle and not a joint, we should do the same with the waist. (We don't think of bending the arm at the bicep - we bend it at the elbow - we just use the bicep to do it.)
If the waist was a joint, there would be clear skeletal structure to support the theory.
Here is a series of images that shows the musculature of the torso. The waist is an effect, not an actual muscle.
I know it seems like I'm really going off the deep end with this whole "no waist" bit, but it actually really matters to us as percussionists. If our instruments are not at a correct height, we will often bend at the waist to maneuver our arms into a more comfortable playing position. Of course in doing that we are forcing the thoracic vertebrae to bend, which they can't do for long without eventually straining the ligaments and muscle around them, so then our backs hurt.
Instead of thinking that we should "play through the pain," let's just avoid it in the first place.
Here We Go
The spine, one of nature's many miracles, is made of 33 vertebrae: 24 are stacked and separated by discs, and the last nine (at the base of the spine essentially "inside" the pelvis) are fused together to form the sacrum and coccyx. The 24 movable vertebrae are divided into regions, each of which slightly different characteristics and obligations.
 |
| source |
The thoracic region is responsible for a great deal of the flexibility, mobility, and rotation we can accomplish; this region's accentuated curve is well-suited to its function for movement.
The lumbar region, made of thicker and larger vertebrae, is designed for weight-bearing support and balance. The lumbar vertebrae are the least flexible, but that does not mean they aren't able to move, they can - it's just not so noticeable to us, much like we don't notice the collar bone's movement when we move our arms. (Read more about that in my article in the October 2015 issue of Rhythm!Scene.)
The cervical region makes up what we think of as the neck, and its vertebrae are tiny in comparison to the lumbar vertebrae. TINY. The top of the spine is meant to balance the head, not to hold it up - that's too much work for those little bones and muscles (more on them later). If you look at the posterior view, you will see two small "ruts" at the top of the cervical vertebrae - this is where the skull balances. The cervical vertebrae, though not meant to hold up weight, are still mobile - try to tilt your head forward, back, and to each side - the cervical vertebrae make this possible.
Here is a diagram showing the relationship of the spine with the pelvis.
 |
| source |
1- it shows that the sacrum and coccyx extend into the pelvis, descending all the way to the level of the hip joint;
2- it shows the size of the lumbar vertebrae (they are each about a third of the size of an ilium!!!); and 3- the discs between our mobile vertebrae are portrayed as bouncy, vibrant organisms.
More About Discs
The spine is not glued together. A healthy, uninjured spine has dynamic disks between vertebrae, aptly named intervertebral discs. Think of them like shock absorbers. Just like shocks on a car keep it from bottoming out on the potholed lanes of Mass Pike, Storrow Drive, or any other street [not necessarily in Boston], our discs make sure that our strategically-shaped vertebrae don't slam against one another or down onto the pelvis, which could result not only in a slipped disc or broken pelvis, but perhaps a disconnection of the nerves in the spinal column. Particularly when located in the lumbar region of the spine, a slipped disc means incredible discomfort.
Where Does the Weight Actually Go?
To understand where the weight is distributed along the spine, it is best to look at a vertebra individually from a bird's eye view.
 |
| source |
By touching the middle of your own lower back, you can imagine the size of the spinous process, and from there you can imagine the size of the vertebral body and its distance from the spinous process. I imagine there being anywhere from 1.5-2 inches between the tip of the spinous process and where weight is actually distributed throughout my spine.
A correct mental image (see: body map) is key to learning how the spine aligns and balances rather than holds. A common misconception is that "good posture" results from a straight back; from looking at the natural curve of the spine, it is clear that balance is not achieved by a straight line, but instead by properly distributed weight. If we measure the idea of a straight back by imagining the bony protrusions (aka spinous processes) on our backs, we are trying to hold up our entire torso with the attachments of muscles and ligaments rather than balancing it a few inches inward on the long column of stacked vertebral bodies.
The diagram below shows just one example of bad posture. The good posture example shows a more natural spinal curve; you can examine the exaggerated curves of the bad posture model and see that the weight (represented by the vertical line) is placed on the spinous process of the lumbar vertebrae - undoubtedly, this person experiences lower back pain. Notice, too, that the weight is placed on the front of the hip and the back of the neck. This person probably experiences pain there, too.
 |
| source |
The example of good posture shows the line of weight distribution closer to the midline of the body, in line with the hip joints, the back of the knee, and the pons at the top of the cervical vertebrae where the skull delicately balances.
Ain't Nobody Have a Waist
The waist is the smallest circumference of the torso. Throughout history we have celebrated the tiny and if they weren't already, we tried to make them appear to be.
 |
| source |
What's interesting is that there is no anatomical body part that constitutes as a waist-maker. The waist is an effect of the toning of obliques, lats, abs, and other little muscles that happen to cross at the lower end of the rib cage. This is all probably obvious, but what's interesting is that we sometimes think of this muscular accident as a joint, moving our torsos in relation to it, which makes us look like the bad posture example from above, causing back pain. If we are able to view the bicep as a muscle and not a joint, we should do the same with the waist. (We don't think of bending the arm at the bicep - we bend it at the elbow - we just use the bicep to do it.)
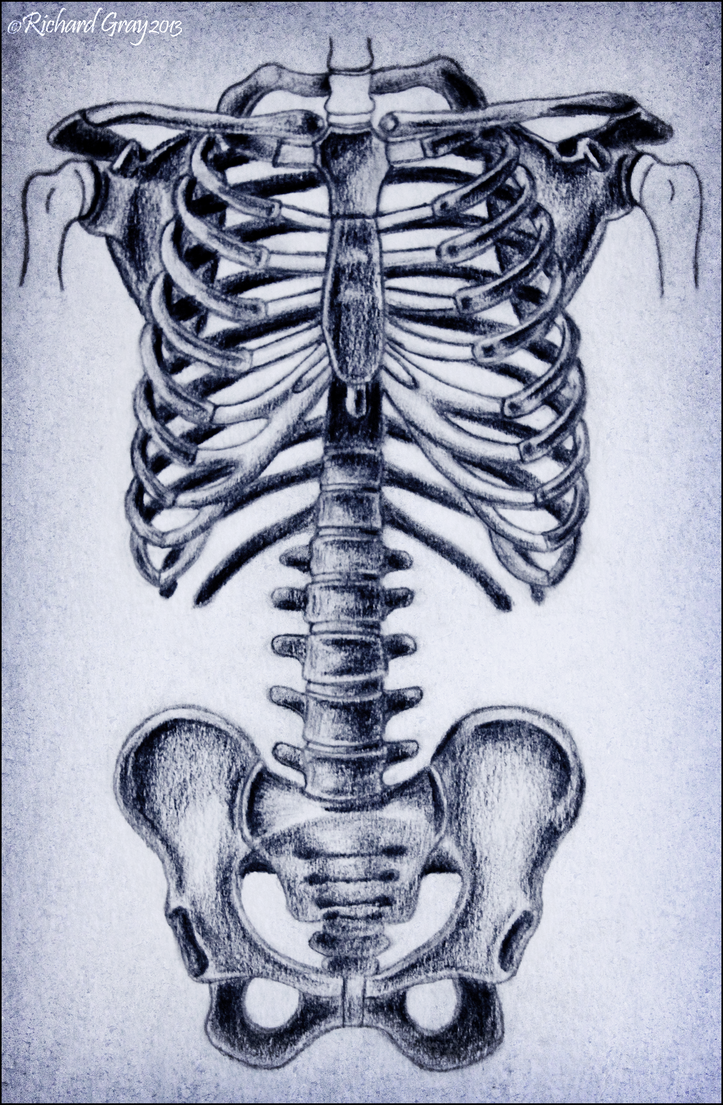 |
| There is beautiful symmetry in this hand-drawn image. source |
Here is a series of images that shows the musculature of the torso. The waist is an effect, not an actual muscle.
 |
| source |
 |
| source |
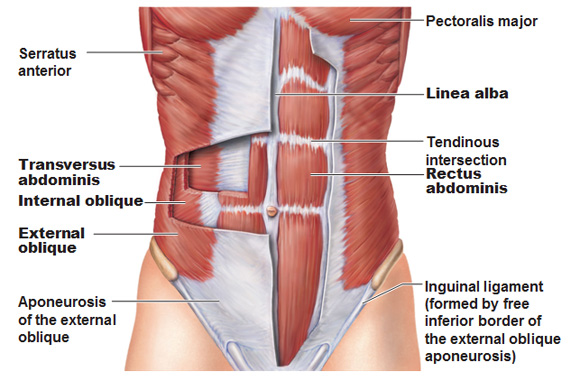 |
| source |
I know it seems like I'm really going off the deep end with this whole "no waist" bit, but it actually really matters to us as percussionists. If our instruments are not at a correct height, we will often bend at the waist to maneuver our arms into a more comfortable playing position. Of course in doing that we are forcing the thoracic vertebrae to bend, which they can't do for long without eventually straining the ligaments and muscle around them, so then our backs hurt.
Instead of thinking that we should "play through the pain," let's just avoid it in the first place.

You've written really nice article with great information and beautiful way of explanation about spine discs. As a chiropractic care it's very useful for me.
ReplyDelete